What Is E-Bike System
How An E-Bike Works
An e-bike system consists of several electronic parts, including a motor, battery, sensor, controller, and HMI. The key to creating a perfect e-bike is ensuring that all components work well together.
The motor, the heart of the e-bike, gives you a boost and makes initial acceleration much easier, helping you keep up to speed. Its power is from a rechargeable battery mounted on the bike.
When pushing the pedals, the sensor measures the speed and how much effort you put in, delivering the signals to the controller. Analyze and discern the riding status and make the motor provide precise power output to maintain a natural “bike-like” experience—the pedal-assist stops when stopping pedaling or over the e-bike’s preset speed limit.
The rider needs an HMI to control the e-bike, usually mounted on the handlebar or integrated within the frame, deciding how much assistance you want and showing the bike status, letting you effectively achieve your planned ride distance.
The fantastic integrated e-bike system provides all the assistance required for a smooth ride.
Differences Between
Hub Drive & Mid Drive Systems
Hub Drive
The hub-drive system comprises a motor, battery, controller, sensor, and HMI. As the name suggests, the motor directly applies torque to the front or rear hub axle and operates independently of your bike’s drivetrain.

Generally, the hub-drive system makes you feel like they are pushing (rear hubs) or pulling you (front hubs) along. When riding on flat ground or slight climbing, the strong power directly acting on the wheels makes the e-bike rider feel more effortless. It makes hub-drive systems ideal for urban rides, commutes, touring, road racing, and more accessible off-road leisure rides.
Moreover, Hyena’s premium hub drive system uses high-quality torque sensors and advanced firmware algorithms to make e-bikes feel more natural to ride, just like mid-drive systems.
Mid Drive
Except for the battery and HMI, the motor, controller, and sensor of the mid-drive system are integrated into one unit and directly drive your bike’s front chainring, which in turn drives your drivetrain (chain and gears).
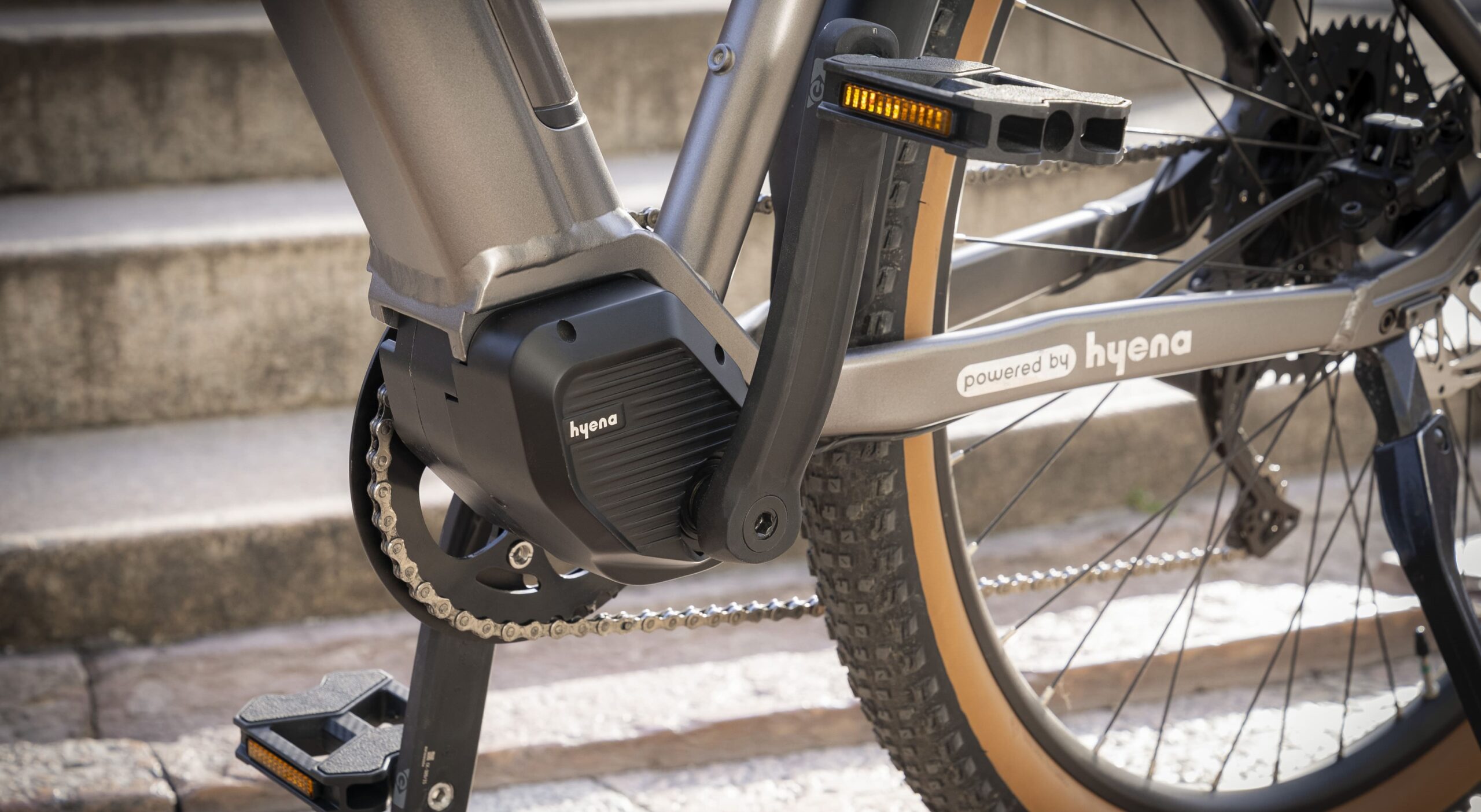

Apply force to the drivetrain in conjunction with the rider’s pedaling; the mid-drive’s biggest advantage over a hub drive is that it can take advantage of your bike’s gears, especially good at low speed/ high torque going uphill, and will use less power doing so. This also makes the mid-drive system generally deliver a better nature-riding feel. These features make the mid-drive systems more suitable for bikes that need higher torque to face undulating terrain and off-road such as MTB, advanced touring, and cargo bikes.
Also, experience riders can use the bike’s gears to keep the motor running at the most efficient RPM when riding the mid-drive e-bikes. In this case, mid-drive e-bikes offer more range than hub-drive ones.
What Should You Notice
For E-Bike Design
In addition to how the drive system works and the ride feel they delivered, if you are a designer or manufacturer of bicycles, you will want to consider more before choosing between hub drive systems and mid-drive systems.
Bike Frame Design

The mid-drive system requires a special motor mounting bracket to replace the bottom bracket area, which makes the frame design more complex.
For the hub drives, you need to ensure the OLD fits the motor. For both, you also have to consider the chain line, the frame design to accommodate the battery, and the bike’s center of gravity in relation to the drive system components.
Drivetrain

Rear hub motors can’t be used in conjunction with internal gear hubs; they only work with freewheel or cassette. Also, you might need a special chainring set to adapt to the mid-drive shaft or BB sensor (hub drive).
Bike Maintenance

Mid-drives put stress on drivetrain components, so the wear of the bicycle drivetrain will be relatively higher than that of the hub drive systems.
Throttle

Because it directly drives the wheels, hub drive systems are better for working with the throttle. Also, for the regions/models which allow equipping throttle, you can choose a hub motor with higher output power.
Remember to check your local regulation regarding the throttle availability and if the brake cut-off sensor is necessary.
Overall, the hub drive and mid-drive systems have advantages and disadvantages. Different bicycle categories and rider behaviors will affect your choice, depending on how you would like your bike to be used. For example, the riders might not really need a mid-drive for commuting short distances when they are more focused on effortless, easy rides with drive system support; on the contrary, if a hub drive system is used on an MTB, it will be less effective than a mid-drive system.
Having Difficulty Choosing?
With a decade of experience in e-bike projects, the Hyena team is your strongest backup for e-bike development, certification, to after-service.
For every e-bike project idea brought up, we provide drive system products and development consultation and then help our business partners complete their e-bikes step by step with technical support. Whether you want to have a tech chat or start a project, we’re here for you.